Business Process
Introduction
At the heart of every company there's a business process that orchestrates the main activities that are implemented. Conduite is built for service delivery and consulting organizations that:
- Conduct business in 2 main phases:
- Business Development / Sales - You manage a pipeline of opportunities that eventually turn into contracts and projects you execute.
- Execution - You deliver work according to a contractual scope of work.
- Sell mostly people's time (labor) based on daily rates
- Manage financial objective based on opportunity and contract margins.
For each of these phases, Conduite provides apps and KPIs that help you manage and track the health of your business.
Overview Of The Process
The overall business process can be broken down in 5 steps. It shows show the Conduite apps to support its implementation.
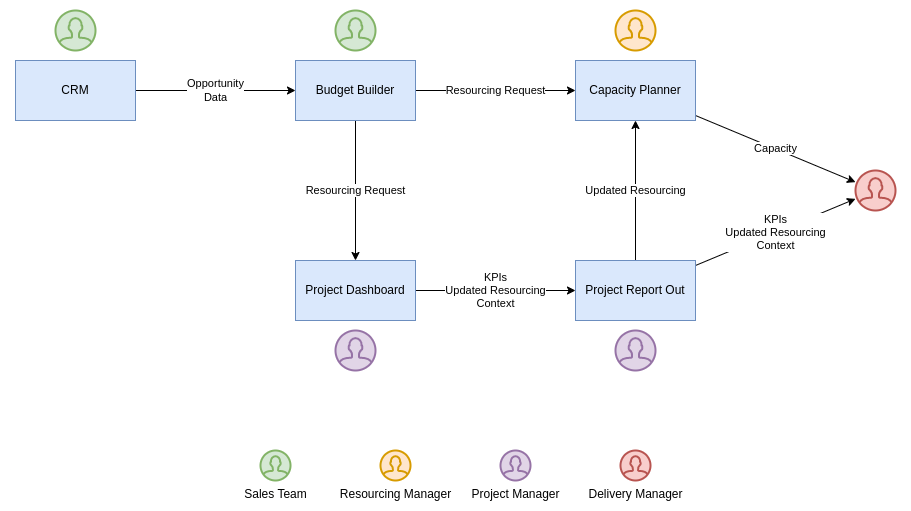
Data Flow Between Apps & Key Roles
1. Develop An Opportunity
Business Development
Your Sales Team develops leads that eventually become opportunities. You manage these opportunities with a CRM in which you qualify key attributes such as client name, amount, probability, start date and duration. The Sales Team keeps updating these attributes as discussions go with the prospects.
What is a Sales Team?
The Sales Team is a group of people in charge identifying potential clients (prospects) and to sell them the services that your company offers.
2. Create & Update The Offer
Business Development
If successful, your Sales Team will convince your prospect to send an offer. You start preparing a document with the appropriate narrative (methodology, risk analysis, ...), budget and timeline. In order to produce the two latter elements, you use a Budget Builder that helps you plan over time the number of days for each role (or person) needed to execute the scope of work. That tool also provides you with the margin you can expect to make on this contract.
In order to secure the availability of the required roles in the event you win the opportunity, your Sales Team sends a Resourcing Request (days / role / period) to your Capacity Manager. S/He can pencil that workload into the Capacity Planner and starts working on potential resourcing conflicts. The Resourcing Request includes the probability of the opportunity so that the expected workload can be weighted.
What is a Capacity Manager?
The Capacity Manager (or Resourcing Manager) is the person who's job is to make sure that there is a consolidated view of who's working on what and when (present and future). As the main resource of your company is people's time, this is an essential function. It will allow you to know whether you have too much work coming up and need to hire, or if you need to make adjustments to manage a slowdown in activity.
As discussions evolve with the prospect, your Sales Team send updated Resourcing Requests to your Capacity Manager in order to for her/him to have the latest information.
3. Sign The Contract & Kick Off The Project
Execution
You've won the opportunity! 🎉 You endure the final administrative hurdles and sign the contract. It's time to kick off the project and set up the internal tooling. You need to configure your Project Dashboard that will help you track the execution of the project with the financial data from the contract (total amount, labor amount, expenses amount, expected margin) and with the most up to date Resourcing Request. That last piece in very important since you want to know how you team is doing against the initial plan.
At this point you can hand over the project to a Project Manager and start executing the scope of work.
What is a Project Manager?
The Project Manager is the person accountable for the proper execution of the project. S/He has to ensure that the client is happy with the work that is being delivered, that the financials of the project are under control and that her/his own team is happy. It's a role that requires a versatile mix of skills (technical, organizational, relational). Project Managers are key to the success of projects.
4. Manage The Project
Execution
Your team is actively working 🛠️, i.e. spending days, on the project. It's important to have regular updates on how things are progressing in order to avoid bad surprises. You ask your Project Managers to update their Project Dashboards on a regular basis with how much time each person has spent on the project and with how many days s/he thinks will be required to deliver the expected scope of work, i.e. an updated resourcing. The Project Dashboard consolidates this updated information and feeds it back the Project Manager in the form of KPIs that tell her/him how s/he's doing financially.
Your Delivery Manager needs to centralize these updates in order to build a global overview of the situation. You ask your Project Managers to send a Project Report Out that includes specific KPIs from the Project Dashboard, the updated resourcing and a short narrative on what happened in the last period to give context to the numbers. The labor forecast goes the Capacity Manager that can update the Capacity Planner accordingly.
What is a Delivery Manager?
The Delivery Manager is a person in charge of overseeing execution (delivery) of projects. This is a senior role with strong Project Management skills and experience. S/He feeds off the regular project updates to trigger corrective actions in support to Project Managers. S/He is often accountable for the improving the way projects are executed. This role is often combined with the one of Capacity Manager.
With this update cycle in place you are able to keep track of projects (push corrective actions and/or praise colleagues) and of your capacity at all times.
5. Close The Project
Execution
After a lot of hard work, countless client meetings and presentations the project comes to an end. The client is happy 🤩 (or not 😡). Your team organizes a project retrospective in order to learn from what went well and what went wrong.
The Key Metrics
Conduite apps provide a limited, yet powerful, number of metrics that allow you to track and manage the health your business. Most of the KPIs produced by Conduite apps are related to the margin objectives that you want to achieve during the business development and execution phases.
Definition of Margin
{{@15}}
This is central feature of Conduite as it assumes a certain structure for your budgets.
Business Development Phase
Conduite CRM provides the Expected Value (EV) of your Business Development pipeline. It is the dollar amount that corresponds to the sum of the value of the opportunities weighted by their probability. In addition you get:
- The distribution of that Expected Value over time
- The distribution of the margin part of that Expected Value over time
This gives you a good idea of how much business in being generated. The Expected Value has a capacity equivalent that you can mostly find in the Capacity Planner. Mostly because not all opportunities have a corresponding Resourcing Request.
Execution Phase
During execution your main concern is not know whether your project is over (or under) budget. The Project Dashboard is focused on answering that very question. I provides a single KPIs for that: Execution Efficiency (EE).
It measures how efficiently your team is executing a project with respect to the margin objective they have. If they are 100% efficient it means that they will achieve 🎯 the margin objective. If they are below 100% 👎, they will not achieve it. If they are above 👍, they will surpass it.
Execution Efficiency is a powerful KPI because it is relative to the margin objective. The latter might change over the course of a project but the team always knows that they need to hit 100% EE or above. That is the only KPI your team needs.
